Describe the Process of Dna Replication Including Enzymes
The DNA polymerase attaches to the unwound strands of DNA but this enzyme can only extend the primer from. The following points highlight the three main enzymes of DNA replications.
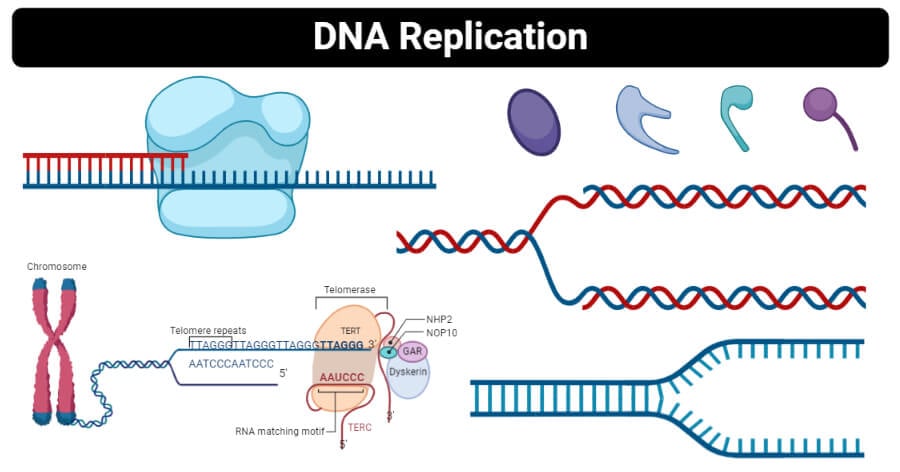
Dna Replication Definition Enzymes Steps Mechanism Diagram
Students will be able to.
. Leading and lagging strands and Okazaki fragments. Describe the process of DNA replication including the enzymes involved 85 and give two examples of drugs or toxins that affect the process 15. We begin our investigation by describing the basic model for how nucleotides are joined in a specific order during DNA replication.
Exonucleases - group of. DNA synthesis starts at specific points called Origins which are located within the DNA strand. Initiation at the origin of replication unwinding to expose the strands synthesis on both strands with many enzymes adding nucleotides 3 to 5.
Roles of DNA polymerases and other replication enzymes. Prokaryotic DNA Polymerase. Describe the process of DNA replication.
It forms the replication fork by. DNA primase - a type of RNA polymerase that generates RNA primers. This is the list of Enzymes Involved in DNA Replication.
STAGES OF DNA REPLICATION Initiation initiated at ori C origin of chromosomal replication unwinding of double helix forming a replication fork helicase which opens up the helix single-stranded binding proteins SSBP stabilize the single-strand. DNA replication involve the generation of a new molecule of nucleic acid DNA crucial for life. The central enzyme involved is DNA polymerase which catalyzes the joining of deoyribonucleoside 5-triphosphates dNTPs to form the growing DNA chain.
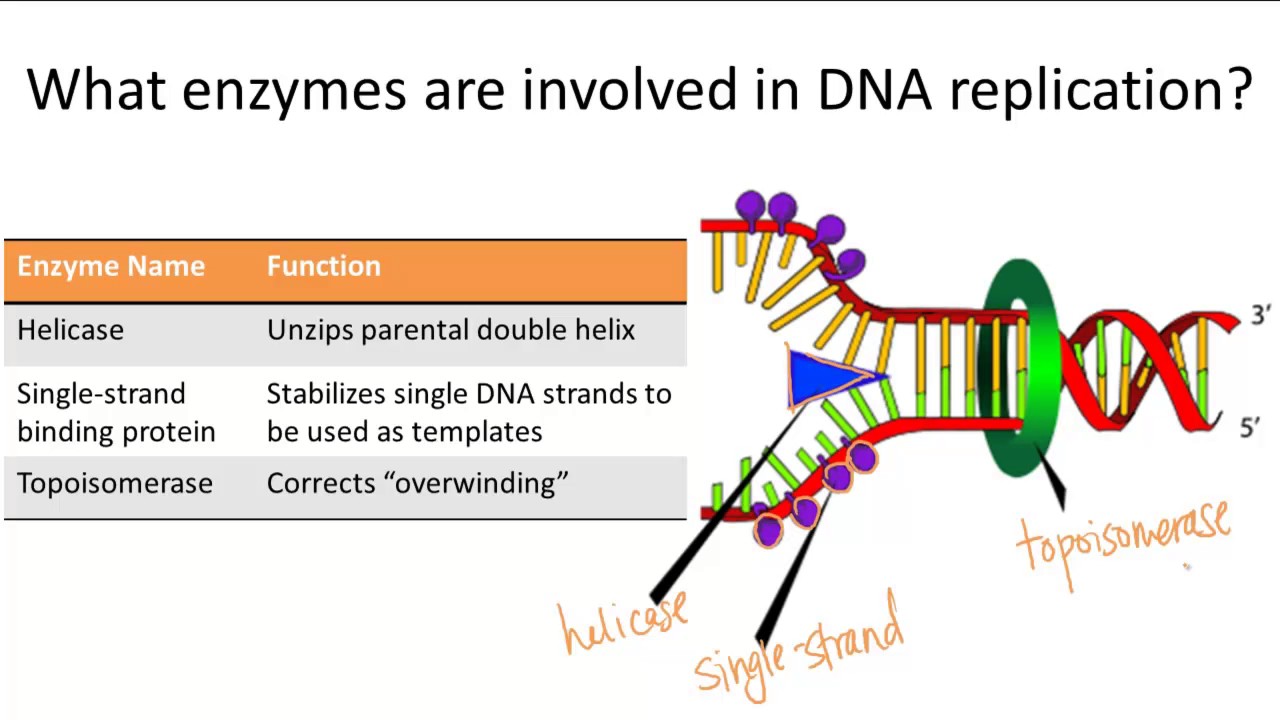
Be sure to include all enzymes and their functions. Helicase begins to unwind the DNA at the ORIGIN OF REPLICATION a specific DNA nucleotide sequence Its common to only show one strands sequence of bases since the other can be. Topoisomerase or DNA Gyrase - unwinds and rewinds DNA strands to prevent the DNA from becoming tangled or supercoiled.
DNA polymerases - synthesize new DNA molecules by adding nucleotides to leading and lagging DNA strands. DNA polymerase III ATP GTP TTP CTP DNA polymerasre III can only add nucleotides to 3 end of a growing DNA strand. DNA replication is the process of producing two identical copies of DNA in which each template for the synthesis of a new complementary daughter strand.
Be sure to include all enzymes and their functions. A primase is an enzyme which makes the RNA primers required for initiation of Okazaki pieces on the lagging strand. DNA replication occurs in a series of five steps.
This process is made possible by different enzymes including DNA helicase to separate the two strands DNA polymerase to synthesize a new strand of DNA and DNA ligase to join DNA fragments together. This process is monitored and controlled by the DNA replication enzymes. In your description include when during the cell cycle DNA replication takes place.
Basic Mechanisms of Replication DNA replication is semiconservative. Today DNA research has revealed intricate details of how the genetic code is copied or duplicated during cell division. Primers are short RNA molecules that act as templates for the starting point of DNA replication.
It is also necessary for evolution and immune system response. -The two strand DNA divides. Basic process and enzymology of DNA synthesis and the next chapter will cover regulation of DNA replication.
DNA replication process uses DNA polymerase as the main enzyme for catalyzing the joining of deoxyribonucleoside 5-triphosphates. Primers are short RNA molecules that. It conserves the entire genome for the next generation.
DNA replication is a fundamental genetic process that is essential for cell growth and division. Science Biochemistry QA Library Describe the process of DNA replication including the enzymes involved 85 and give two examples of drugs or toxins that affect the process 15. DNA molecule has a double helix structure with two strands of nucleotides coiled together and held in place by a 2-deoxyribose sugar-Phosphate backbone.
During DNA replication molecules that line up along the unpaired DNA strands holding them apart while the DNA strands serve as templates for the synthesis of complimentary strands of DNA Explain the roles of DNA polymerase mismatch repair enzymes and nuclease in DNA proofreading and repair. These are special unwinding enzymes that help in breaking the weak hydrogen bonds which hold the two strands together. DNA replication is an essential part of cell division as it ensures that each new cell has the same genetic information.
Enzymes that participate in the eukaryotic DNA replication process include. 29 Describe the process of DNA replication including leading and lagging strand from HAP W05 at Little Elm H S. Let us discuss this in detail Single-Stranded Binding Protein SSBP DNA Helicases.
Describe the process of DNA replication including the roles of major enzymes Table 111 involved in particular steps. Describe the process of DNA replication. DNA replication is a semiconservative process where a parental strand template is used to synthesize a new complementary daughter strand using several protein elements which include enzymes and RNA molecules.
This extension of new DNA strands. Recall the basic structure of DNA including the complementary base pairings describe the process of semiconservative DNA replication explain the role of DNA helicase DNA polymerase and DNA ligase in semiconservative DNA replication describe how errors introduced in DNA replication can be corrected. If youre seeing this message it means were having trouble loading external resources on our website.
DNA helicase - unwinds and separates double stranded DNA as it moves along the DNA. The enzymes involved in the process of DNA replication are as follows. Single-Stranded Binding Protein SSBP SSBP means Single-Stranded Binding Proteins.
DNA replication is the process of making new copies of DNA from an original molecule of DNA. DNA replication is important for properly regulating the growth and division of cells. Helicase -The single strands then get the single stranded binding proteins attach to prevent the single strands from becoming a double helix again at the replication fork.
DNA Replication Initiation.

Enzymes Involved In Dna Replication Youtube
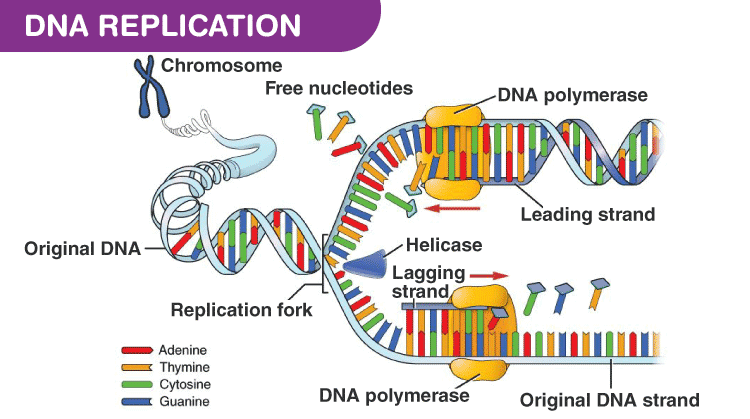
Dna Replication Process With Diagrams Class 12 Prokaryotic Eukaryotic Dna Replication

Comments
Post a Comment